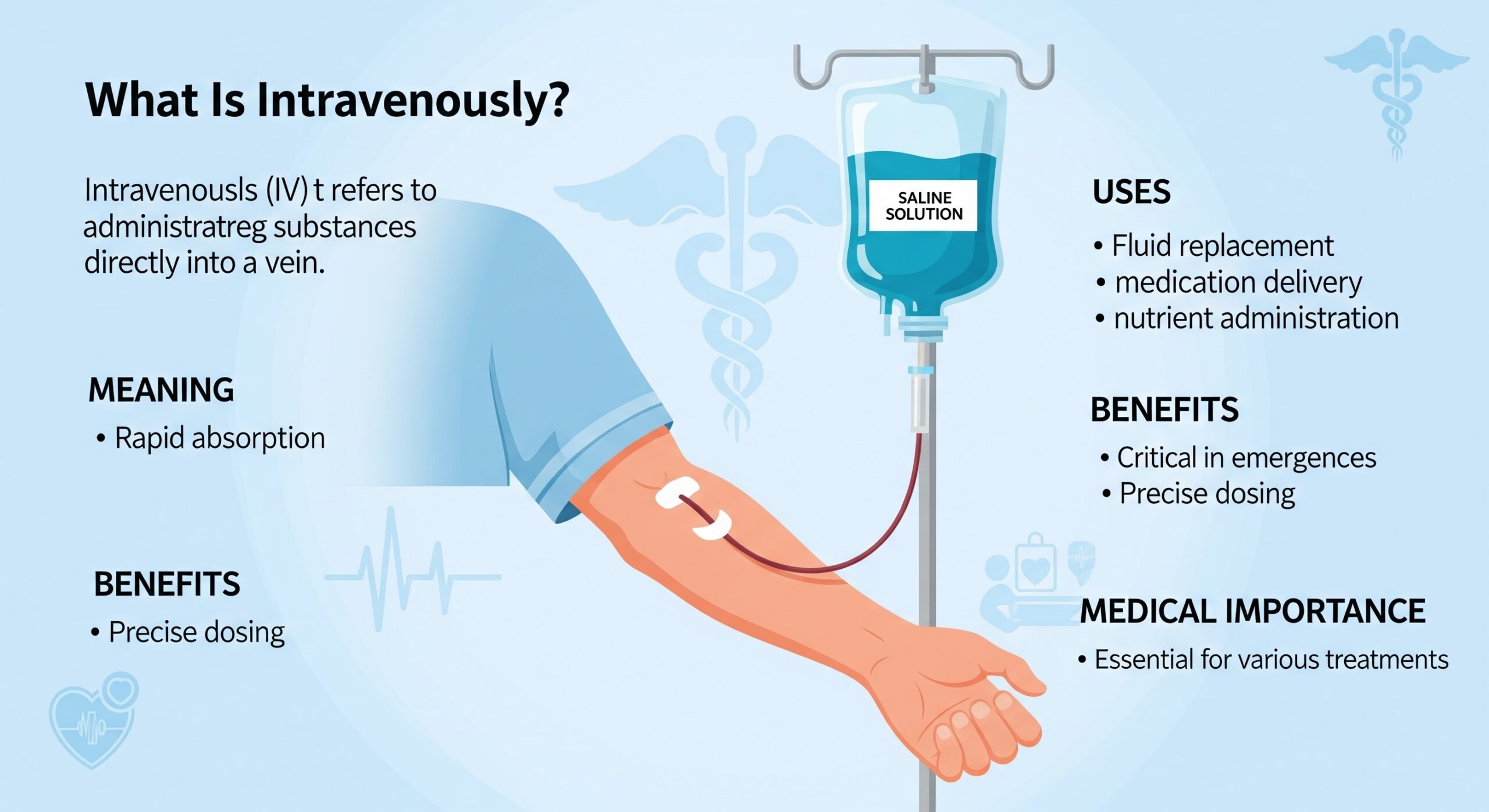
Modern healthcare depends on precise and effective methods of delivering fluids, nutrients, and medications to the body. One of the most trusted and widely used techniques is intravenous administration. When patients, caregivers, or healthcare students ask what is intravenously used in medicine, they are referring to a method that delivers substances directly into the bloodstream through a vein, ensuring rapid absorption and immediate results.
From emergency rooms and intensive care units to outpatient clinics and mobile wellness services, intravenous therapy plays a critical role in saving lives and improving patient outcomes. This in-depth guide explains everything you need to know about intravenous administration, its benefits, uses, safety considerations, and growing role in modern healthcare.
What Does Intravenous Administration Mean?
Intravenous administration is the process of delivering fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into a vein. Because the substance enters the bloodstream immediately, it bypasses the digestive system entirely. This allows healthcare providers to control dosage accurately and achieve faster therapeutic effects.
This method is commonly abbreviated as “IV” and is one of the most efficient routes of administration available in medical practice today.
How Intravenous Therapy Works in the Body
Once an IV catheter is placed into a vein, fluids or medications flow directly into circulation. From there, they are rapidly distributed to vital organs such as the heart, brain, kidneys, and liver.
Key Components of an IV Setup
-
Sterile IV catheter
-
Medical-grade tubing
-
Fluid bag or syringe
-
Flow regulator or infusion pump
Each component is designed to ensure safety, sterility, and precise delivery.
Why Doctors Choose Intravenous Administration
Healthcare professionals choose IV therapy when speed, reliability, and precision matter most.
1. Immediate Drug Action
IV medications act almost instantly, making them essential in emergencies like allergic reactions, infections, seizures, or cardiac events.
2. Effective Hydration
Severe dehydration caused by illness, heat exposure, vomiting, or alcohol use is best treated with IV fluids that restore electrolytes quickly.
3. Nutrient and Vitamin Delivery
Patients who cannot absorb nutrients orally may receive vitamins, minerals, or nutritional solutions intravenously.
4. Pain and Symptom Management
IV pain medications offer fast relief and allow careful dosage control.
Types of Intravenous Fluids Used in Medicine
Crystalloid Solutions
These are the most commonly used IV fluids and include:
-
Normal saline
-
Lactated Ringer’s
-
Dextrose-based solutions
They help restore hydration and electrolyte balance.
Colloid Solutions
Used in specific clinical situations such as shock or blood loss, these fluids remain in the bloodstream longer.
Medication Infusions
Antibiotics, antivirals, chemotherapy drugs, and biologics are often administered intravenously for maximum effectiveness.
Intravenous vs Other Routes of Administration
Understanding how IV therapy compares with other methods helps explain its importance.
Oral Medications
-
Slower absorption
-
Reduced effectiveness due to digestion
-
Not suitable for unconscious or vomiting patients
Intramuscular Injections
-
Faster than oral but slower than IV
-
Limited volume capacity
Subcutaneous Injections
-
Slow, steady absorption
-
Used for long-term treatments like insulin
This comparison often leads people to ask what is intravenously administered differently—its key advantage is 100% bioavailability.
Benefits of Intravenous Therapy
-
Rapid symptom relief
-
Complete absorption
-
Accurate dosing
-
Suitable for critical and chronic conditions
-
Ideal for patients unable to swallow
These benefits make IV therapy indispensable in both emergency and routine care.
Risks and Safety Measures
Although IV therapy is generally safe, potential risks include:
-
Infection at the insertion site
-
Vein irritation
-
Fluid overload
-
Allergic reactions
Proper training, sterile techniques, and patient monitoring significantly reduce these risks.
Who Is Qualified to Administer IV Therapy?
Intravenous therapy must be performed by trained professionals such as:
-
Registered Nurses
-
Physicians
-
Nurse Practitioners
-
Certified Paramedics (in specific settings)
Certification and ongoing education are essential for maintaining safety and compliance.
IV Therapy Beyond Hospitals
In recent years, IV therapy has expanded into wellness and preventive healthcare. Many clinics offer IV services aimed at:
-
Boosting energy
-
Supporting immune health
-
Improving athletic recovery
-
Relieving migraines
-
Enhancing skin health
These treatments follow the same medical principles used in hospitals.
How the Body Responds to IV Treatment
Once administered, IV fluids and medications circulate quickly throughout the body. This rapid distribution helps correct deficiencies, reduce symptoms, and support healing more efficiently than other methods.
Many patients report noticeable improvement within minutes, especially after hydration or vitamin infusions.
Common Myths About Intravenous Therapy
Myth: IV therapy is only for emergencies
Fact: It’s widely used for routine and preventive care.
Myth: IV therapy is unsafe
Fact: When performed correctly, it is extremely safe.
Myth: Only sick people need IVs
Fact: IV therapy is also used for wellness and recovery.
Training and Technology in IV Therapy
Advancements in medical technology have improved IV safety and comfort, including:
-
Smart infusion pumps
-
Improved catheter materials
-
Personalized IV formulations
These innovations continue to enhance patient outcomes.
The Future of Intravenous Care
As healthcare becomes more personalized and accessible, intravenous therapy will remain a cornerstone of effective treatment. With mobile IV services, improved training programs, and advanced monitoring tools, patients can expect safer and more convenient care.
Understanding what is intravenously delivered in modern medicine helps patients make informed decisions and appreciate the science behind this powerful treatment method.
Final Thoughts
Intravenous administration is one of the most efficient and reliable ways to deliver treatment in modern healthcare. Its ability to provide rapid results, precise dosing, and complete absorption makes it essential across emergency medicine, chronic disease management, and wellness care.
When patients fully understand what is intravenously used for, they gain confidence in treatment decisions and better insight into how modern medicine supports faster recovery and improved quality of life.